Jigsaw

A jigsaw activity is a cooperative learning technique where students work in groups to teach each other portions of a topic. Subject groups become ‘experts’ on a portion of the content. Then the individuals from each “subject group” rearrange into peer “instruction groups” to share what they have learned.
Why It Works
The jigsaw activity organizes classroom learning in ways that make students responsible both as individuals and team members for mastering subject area content. They are dependent on each others work to succeed. Breaking classes into subject area groups and then re-organizing them into final peer instruction groups makes the process of presenting the final content similar to completing a jigsaw puzzle by "assembling" its pieces. In the jigsaw activity students have to actively “build knowledge” and deliver a final presentation product.
1. Select a larger topic that can be divided into several sub-topics.
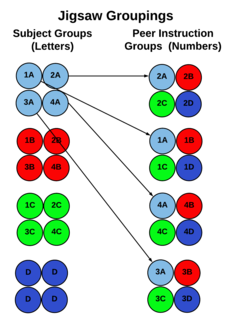
2. Create a Subject Group for each sub-topic that will discuss andsummarize its main points. (See diagram)
3. Rearrange individuals into Peer Instruction Groups so that each group has one person from each Subject Group. (Right side of diagram)
4. Instruct individuals to take turns teaching their Peer Instruction Group members about their sub-topic
5. Optional closing activity: Give students formative assessment questions to answer (as individuals or as groups) to evaluate their learning
Video Exemplars
Gonzalez, J. [Cult of Pedagogy]. (2015, April 15). The Jigsaw Method
[Video file]. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=euhtXUgBEts
Research Evidence
Content Description: Read this for more detail about how Jigsaw was implemented in an undergraduate technical college course.
Perkins, D. V., & Saris , R. N. (2001). A "Jigsaw Classroom" technique for undergraduate statistics courses. Teaching of Psychology, 22, 111–113.